How a Backend for ReactJS Works with Frontend Code
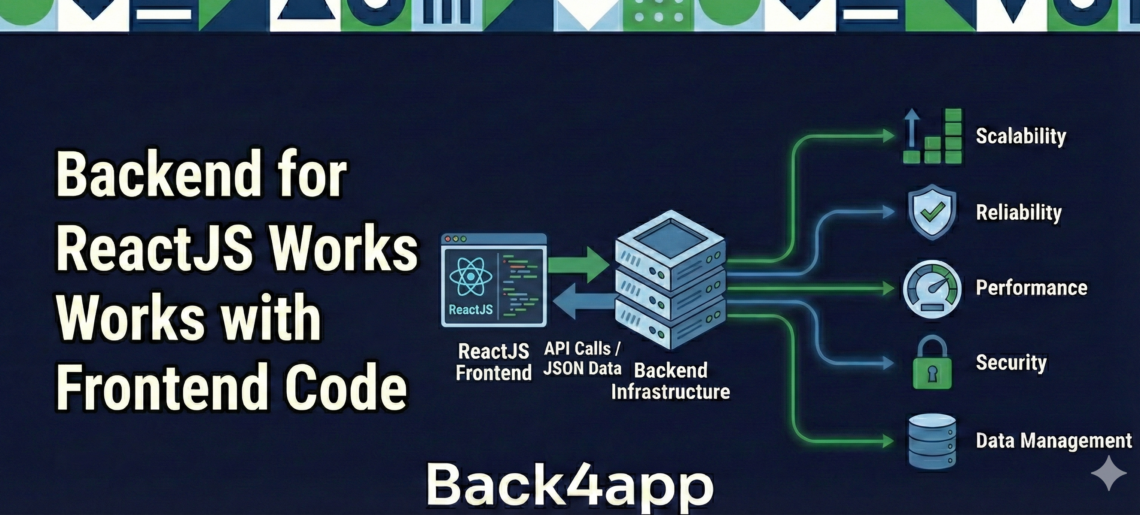
ReactJS makes building websites and apps feel smooth and quick. It takes care of how things look and respond on the screen, from a simple button to a full layout. But the visual part is only half the story. Apps still need to save data, log in users, and update information in real time. That is where the backend comes in.
A backend for ReactJS works behind the curtain. It handles the heavy lifting so the screen your users see can stay fast and clear. When both sides work together, your app runs better and leaves a stronger impression.
Contents
- 1 How ReactJS Handles the Frontend View?
- 2 What the Backend Does Behind the Scenes?
- 3 How ReactJS and Backend Talk to Each Other?
- 4 Why a Good Backend Makes Frontend Code Even Better?
- 5 Powering Up Your App with the Right Help
- 6 Why does a ReactJS application need a backend?
- 7 How do ReactJS and the backend communicate?
- 8 Does a slow backend affect the performance of my React frontend?
How ReactJS Handles the Frontend View?
ReactJS is all about making the screen feel alive. When someone clicks a button or types in a message, ReactJS knows exactly what to show and how quickly to show it. It does this using components. Each part of the screen, like a menu bar, form field, or card, is its own part called a component.
These components know how to display information and how to update themselves when something changes in the app. So if a user enters a name or picks a date, ReactJS handles that on the screen. But where does that information go? That is where the backend takes over.
Components in ReactJS are reusable and modular, which makes building complex user interfaces practical and efficient.
For example, a calendar on a dashboard or a chat window in a messaging app both can be managed easily due to React’s clear system for updating only what changes, keeping the interface lightning fast for the user.
ReactJS keeps all these elements in sync, meaning users rarely encounter lag or confusing transitions, allowing for a modern, app-like experience in the browser.
What the Backend Does Behind the Scenes?
The backend is the quiet part of the app that stores everything safely. It saves usernames, messages, pictures, and other important data that users should not lose.
It also handles things like checking passwords or deciding what a user is allowed to see. Without a backend, ReactJS would not know where to send your message or how to save a user’s login. When the backend does its job, it sends the right information back so ReactJS can keep the screen up to date.
A reliable backend ensures that the information you send isn’t just temporarily kept, but is stored securely and backed up for future use. This means users can close the app, open it again later, and still find all their information right where they left it.
The backend isn’t only about storage, though. It acts as the gatekeeper, checking permissions, validating actions, and ensuring private data stays secure. When you need to scale or introduce new features, a flexible backend can grow with your needs rather than forcing you to start from scratch.
How ReactJS and Backend Talk to Each Other?
How do these two sides work together? ReactJS uses APIs to send and receive information. APIs act like messengers. ReactJS asks something, the API carries that question to the backend, and then brings back an answer.
For example:
- A user clicks “submit” on a form
- ReactJS tells the API what the user entered
- The API sends that data to the backend
- The backend stores the information and replies
- ReactJS uses the reply to update the screen
It is a clean back-and-forth. When a backend for ReactJS is built well, this process happens quickly and without errors, making apps feel more polished and easier to use.
APIs used with ReactJS can be RESTful or use GraphQL, depending on the app’s needs. REST APIs are structured around resources and URLs, while GraphQL lets the frontend ask for just what it needs in a single request, making it a favorite for developers wanting efficiency.
ReactJS, by communicating over these APIs, ensures that data shown in the UI always matches the current state on the backend so users are never confused by out-of-date or missing information.
Secure APIs help keep the connection between frontend and backend safe while ensuring the data exchanged is encrypted and protected.
Why a Good Backend Makes Frontend Code Even Better?
Even the best-looking app will not work if it cannot talk to the backend properly. When the backend runs smoothly, the frontend does not get stuck waiting. ReactJS can pull what it needs and show it faster.
A strong backend helps when more users start using the app. It keeps data moving, handles more traffic, and keeps everything safe behind the scenes. From the user’s point of view, it just works. But it only works well when what is underneath is reliable.
As an app grows and the amount of traffic increases, backend performance becomes even more critical.
A slow or unresponsive backend can turn a seamless user experience into a frustrating one, especially if pages are slow to load or fail to update correctly.
Backend optimization techniques, like caching and database indexing, can keep things fast so ReactJS always has fresh data at hand.
Having a reliable backend is also key for robust error handling and for developing features that depend on instant feedback, like notifications or collaborative editing.
Powering Up Your App with the Right Help
ReactJS helps developers move quickly. You get more done without reloading the page or rebuilding the whole app every time something changes. But great frontend code still needs dependable support. That is where backend services step in.
We provide a ready-to-use Backend-as-a-Service for ReactJS, including real-time database updates, easy API creation, and integrated user authentication.
When backend tools handle things like data storage, authentication, and permissions, we get more time to focus on the features we want to create. When the backend fits well with ReactJS, building and updating the app is easier from start to launch.
A backend service ready to work with ReactJS also means you can spend less time on repetitive setup and more on designing what makes your app unique.
Easy-to-configure APIs or dashboards allow changes to be made rapidly, often without needing to deploy loads of new code. This flexibility supports faster prototyping, quicker releases, and easier scaling when your user base expands.
Backend services with solid documentation and clear guides reduce confusion and speed up learning for new team members.
Ready to supercharge your next project with a seamless connection between frontend and backend?
Discover how Back4app can power your innovations with a robust backend for apps that ensures speed, security, and scalability.
Make development effortless and focus on crafting the features your users will love. Start building smarter today and see how easy app creation can be with the right backend foundation.
Why does a ReactJS application need a backend?
ReactJS focuses entirely on the user interface and how things look on the screen. It cannot store data permanently on its own. A backend is necessary to save user profiles, protect sensitive information like passwords, and ensure that data (like messages or settings) is still there when a user logs back in.
How do ReactJS and the backend communicate?
They talk through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). When a user interacts with a React component—like clicking “Save”—ReactJS sends a request through the API. The backend processes that request and sends back a response, which ReactJS then uses to update the screen without a full page reload.
Does a slow backend affect the performance of my React frontend?
Yes. While ReactJS is very fast at rendering, it can only show the data it has. If the backend is slow to respond, users will see loading spinners or lag, making the app feel unresponsive. A well-optimized backend ensures ReactJS has the information it needs instantly, keeping the experience smooth.



