How to Make an App Like Facebook in 10 Steps

Updated: November 2025
Social networks are more than just “hot”—they are foundational digital infrastructure and an integral part of everyone’s daily life. Do you envision creating the next globally-acclaimed social platform?
In that case, leveraging the proven success and structure of Facebook is a smart place to start. With over 3.05 billion monthly active users as of late 2024, Facebook remains the most successful social network and a powerful blueprint for development.
So, how do you successfully develop a scalable social media app like Facebook?
This article reveals the ten vital lessons I learned from a decade of managing a mobile app development company. As a seasoned founder, I’ll share the crucial details you need to transform your app idea into a reality. Following this proven process will save you significant time and budget on your quest to create a profitable social network.
Ready to start developing your Facebook clone MVP? Dedicate the next 10 minutes to this step-by-step guide. The tips provided here will save you a fortune and fast-track your launch.
Contents
- 1 Facebook Overview – The Blueprint for a Social App
- 2 How to make an app like Facebook?
- 3 1. Do Not Start with Coding Right Away (Prioritize Planning)
- 4 2. List your High-Level Goals
- 5 3. Create a list of the Must-Have Features
- 6 4. Select Your Target Platform: Android, iOS, or Cross-Platform
- 7 5. Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype Your App
- 8 6. Code Your App Frontend
- 9 7. Create the Backend of Your App Architecture
- 10 8. Design the App’s Landing Page
- 11 9. Establish an App Analytics Dashboard
- 12 10. Publish Your App to the App Stores
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 How much does it cost to build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for a social media app?
- 15 Why is Backend as a Service (BaaS) the strategic choice for a social app MVP?
- 16 What are the three essential components needed before coding starts?
- 17 Should I launch my social app on Android or iOS first?
- 18 What is the most important Key Performance Indicator (KPI) to track after launch?
Facebook Overview – The Blueprint for a Social App
Before diving into the technical steps, it’s essential to understand Facebook’s blueprint—the platform you are aiming to clone and innovate upon.
What is Facebook?
Facebook is the world’s largest social media platform, created in 2004 as a collegiate networking service before expanding globally. Its core function is a social media service that enables users to:
-
Connect with friends and family.
-
Create and share posts, comments, and media (images, videos).
-
Join public and private groups based on shared interests.
-
Interact with integrated features like games and third-party apps.
Key Features and Usage
The platform’s success is driven by its essential features, which must serve as the minimum viable product (MVP) requirements for your own social network:
-
User Profiles: Detailed personal pages where users register and manage their identity.
-
News Feed: A personalized, real-time stream of content from friends, groups, and pages.
-
Interactions: Tools for commenting, liking, and sharing content.
-
Messaging: The ability to send direct messages to individuals or groups (now often handled by the separate Facebook Messenger app).
Scale and Mobile Dominance (Updated Statistics)
The sheer scale of Facebook highlights the market size you are targeting. Your app must be built to handle massive traffic and prioritize mobile access:
-
Monthly Active Users (MAU): Facebook currently boasts over 3.07 billion monthly active users worldwide, maintaining its position as the largest social network.
-
Meta Family of Apps: The combined reach of Meta’s applications (Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Messenger) exceeds 3.98 billion monthly active people (MAPs).
-
Mobile Priority: Over 81% of Facebook users access the platform exclusively via mobile devices, underscoring the necessity of a flawless mobile-first development strategy.
-
Messaging Scale: The separate Facebook Messenger app is still a giant, with over 1.01 billion monthly active users globally, confirming instant messaging as a non-negotiable feature for any social app clone.
Now that we have established the market leader’s model, we can proceed with the ten practical steps required to build your app.
How to make an app like Facebook?
Here are the ten crucial steps to create a successful social media site and efficiently manage the development lifecycle.
1. Do Not Start with Coding Right Away (Prioritize Planning)
This first step is the most important lesson that will save you a fortune. Do not start your project with coding!
The reason is simple: coding is the most expensive and least flexible aspect of the entire project. Making changes in the planning phase (design, features) is cheap, but making changes in the code phase is costly and time-consuming.
Given the massive financial resources you’ll be committing, you must approach the programming task with great precision. Before hiring developers, you must do your homework:
-
Define the precise user flow and design you want.
-
Finalize the features you need for your MVP.
-
Create sketches, wireframes, and prototypes.
-
Gather feedback from potential users to validate your concept.
By following this planning approach, you will save valuable money and, critically, avoid the pitfall of investing in an app that nobody wants.
💸 Understanding Development Cost Implications – Social networking apps are inherently expensive to develop due to complexity and scaling requirements.
Emerging Development Tools: The recent advent of Vibe Coding Tools, LLM-driven code generation, and advanced low-code platforms offers a powerful opportunity to speed up development and reduce costs, particularly for repetitive or boilerplate tasks. By leveraging these tools strategically alongside a BaaS platform, development teams can focus their expensive hours on custom features that differentiate the app, rather than foundational coding.
Focusing on planning and validation first ensures your expensive developer hours are spent building the right product, not fixing fundamental design flaws.
2. List your High-Level Goals
Wanting to create “something like Facebook” is a massive goal. The first thing you must do is define your high-level goals and, more importantly, your Unique Value Proposition (UVP).
As of late 2024, the Google Play Store hosts over 3.7 million Android apps, and the Apple App Store has over 1.8 million iOS apps. With that huge number of competing applications, your mobile app needs a razor-sharp focus to succeed.
If you do not have clear-cut goals, your app will just end up as a statistic—one of the thousands of apps that fail to gain traction. A lack of purpose often leads to scope creep, wasted development resources, and an inconsistent user experience.
The best approach is to formalize your strategy before development begins. This means clearly articulating:
-
Target Audience: Who are you serving? (e.g., college students, remote workers, fitness enthusiasts).
-
The Problem You Solve: How is your app better or different from established platforms? (Your UVP).
-
Success Metrics: How will you measure success? (e.g., 10,000 active users in the first six months, $X in ad revenue).
We highly recommend using proven, iterative business methodologies to formalize this process, such as applying the Business Model Canvas to map out key resources and costs, or adopting the Lean Startup methodology to quickly test and validate your core assumptions with real users.
Read this article to learn more.
How to make an app? 13 steps for a successful application
3. Create a list of the Must-Have Features
The “Must-Have Features” define the Minimum Viable Product (MVP)—the bare minimum set of functions required to launch your Facebook clone and begin gathering user feedback. Focus on these core pillars first, and avoid feature bloat.
To ensure clarity and development efficiency, group your features into core functional categories:
🌟 Advanced Features to Plan For:
While not strictly required for the first MVP launch, these features drive retention and monetization and should be included in your future roadmap:
-
Payment System Integration: Necessary if you plan to introduce in-app purchases, paid features, or advertising.
-
Elegant UI/UX: Though not a feature, a simple, intuitive, and elegant User Interface (UI) is vital for usability and user retention.
4. Select Your Target Platform: Android, iOS, or Cross-Platform
At this critical stage, you must choose your launch platform. While the initial advice focuses on selecting just one operating system (OS), the most cost-efficient and rapid approach for an MVP today is often to launch on both using a cross-platform framework.
-
Focusing on One OS (Native): Simpler for initial development, cheaper upfront, and delivers the best performance and user experience (UX) tailored to that specific OS.
-
Cross-Platform (Hybrid): Allows you to reuse a single codebase for both Android and iOS, which significantly saves time and money. While this can complicate the initial MVP structure, it prevents the massive cost of developing the app twice later. This is often the superior choice for a budget-conscious, fast-to-market social app MVP.
📈 Current Mobile Market Share (Updated 2024 Data)
The platform you choose should align with your business goals and target demographics.
If you are targeting a massive global user base, Android offers maximum download volume. If your monetization strategy relies on early revenue from in-app purchases or subscriptions, iOS is often the stronger choice.
5. Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype Your App
Before writing any production code, you must digitally blueprint your application. This step is vital for saving time and money, and for achieving crucial market validation.
It is essential to note that wireframes, mockups, and prototypes are not the same:
Following this structured design approach provides numerous advantages that enhance your market validation and save budget:
-
Cost Efficiency: Changing the design is faster and infinitely more cost-efficient than changing code.Development hours are expensive; design hours are not.
-
Early Validation: Prototypes allow you to fine-tune complex functions and features by gathering feedback from potential users before development, ensuring you build the right product.
-
Accelerated Development: A finalized, interactive prototype acts as the single source of truth for developers, eliminating ambiguity and speeding up the coding process.
-
Accessibility: You can often DIY (Do-It-Yourself) the wireframing and prototyping using intuitive design tools, further controlling early-stage costs.
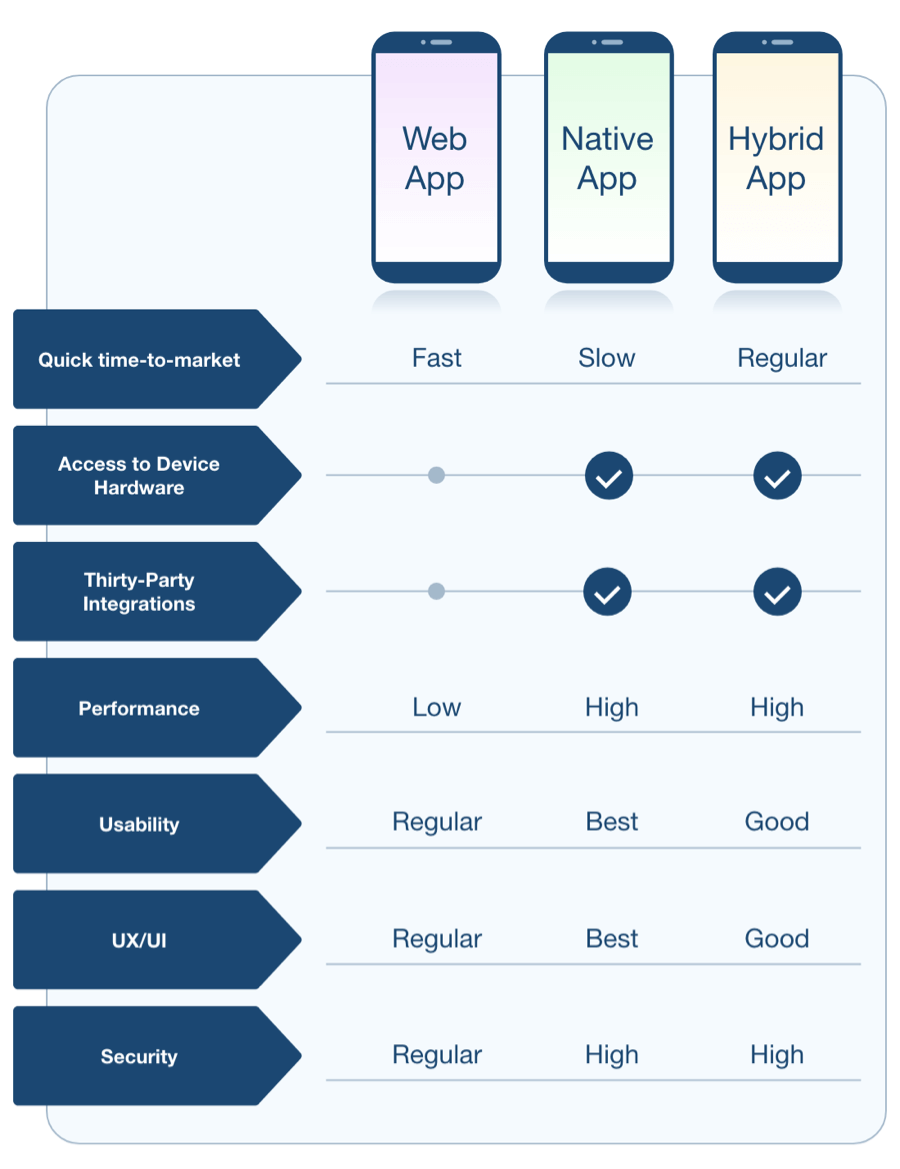
6. Code Your App Frontend
The frontend is the user-facing portion of your application—what the user sees and interacts with. A clean, attractive, and functional appearance is a vital factor in app success and user retention.
You must decide on your approach: developing a Native, Web, or Hybrid Mobile app.
Frontend Development Options
Recommendation for MVP: We prefer the Hybrid app approach for developing an MVP. Its benefits include:
-
It is easier to streamline development for both Android and iOS simultaneously.
-
It is significantly more cost-efficient compared to building two separate native apps.
-
The user experience is superior to pure web apps and maintains offline functionality.
🤖 Accelerating Frontend Development with Vibe Coding
The task of coding the frontend—creating reusable components, managing state, and implementing responsive design—can be significantly accelerated by modern tools.
Vibe Coding (AI-driven coding assistants) and advanced component libraries can help developers generate boilerplate code, suggest optimal UI elements, and quickly translate design files into functional code.
By integrating these tools, you can reduce the manual coding effort, allowing your developers to focus on custom logic and unique UX interactions that set your app apart.
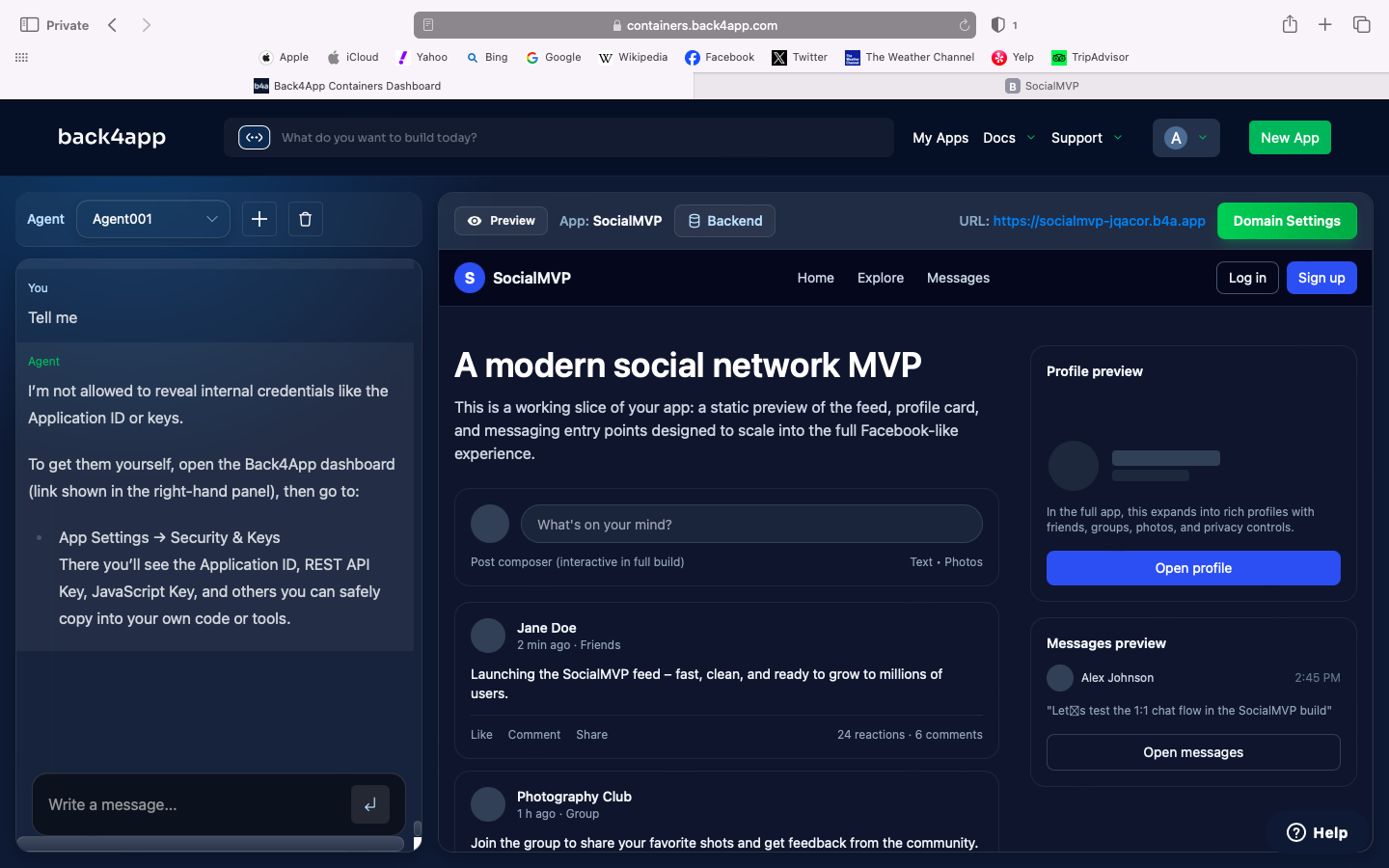
Here is an example of how you can use Back4app agent to create a fully functional Facebook-like application with just a prompt.
Type the prompt below in the agent:
Build a full-featured social networking web and mobile app similar to Facebook. Do not decide or mention any specific tech stack; focus only on product behavior, UX, and functional requirements. Deliver a production-ready MVP with clean, modern UI and scalable architecture.
Core goals
-
Enable people to connect, share content, discover communities, and message each other in real time.
-
Prioritize performance, privacy, safety, and intuitive navigation.
-
Design for millions of users with a clear path to scale.
User roles
-
Guest (not logged in)
-
Registered user
-
Page/Group admin
-
System admin/moderator
Authentication & onboarding
-
Email/phone sign-up, login, logout, and password reset.
-
Optional social sign-in placeholders (no implementation specifics).
-
Email/phone verification flow.
-
First-run onboarding: pick name, photo, bio, interests, and suggested friends/pages.
-
Basic account security settings (change password, active sessions, 2FA placeholder).
Profiles
-
User profile with cover photo, avatar, bio, location, work/education, and “About” sections.
-
Tabs: Posts, Photos, Friends, Groups, Likes/Following, About.
-
Privacy controls per field (Public / Friends / Only me).
-
Ability to view other profiles with mutual friends and shared groups.
Friend system
-
Send/accept/decline/cancel friend requests.
-
Follow/unfollow users (separate from friendship).
-
Friend lists and custom lists (Close Friends, Restricted, etc.).
-
Friend suggestions based on mutual friends, contacts placeholder, and interests.
Feed & posts
-
Main feed with ranked posts (recency + relevance signals), plus a “Most Recent” toggle.
-
Create posts with: text, images, video, links, location, feeling/activity, tagged friends.
-
Post audience selector: Public / Friends / Friends except… / Specific friends / Only me.
-
Edit/delete posts; history not required for MVP.
-
Infinite scroll with smart pagination and loading skeletons.
-
Save/bookmark posts and view saved list.
Interactions
-
Like/Reactions (Like, Love, Haha, Wow, Sad, Angry).
-
Comments with nesting (1 level deep), edit/delete, reactions on comments.
-
Share to feed, to group, or via message; allow quote-share.
-
Basic engagement counters and “who reacted” list.
Stories
-
24-hour disappearing stories (photo/video/text overlay).
-
Story viewer with next/previous, pause, and reaction/reply.
-
Story privacy (Public/Friends/Custom).
Groups
-
Create group: name, description, cover, category, privacy (Public/Private/Hidden).
-
Invite members, approve requests for private groups.
-
Roles: admin, moderator, member.
-
Group feed, pinned posts, membership list, basic rules section.
Pages
-
Create public pages for brands/creators.
-
Page profile with posts, about, photos, followers count.
-
Page admins can post as the page.
-
Users can like/follow pages.
Messaging
-
1:1 and group chats.
-
Real-time sending/receiving, typing indicators, read receipts, online/offline presence.
-
Messages: text, images, emoji, reactions, reply/forward.
-
Chat list with search and unread badges.
-
Basic spam/block controls.
Notifications
-
Notification center and push/in-app notifications for: requests, reactions, comments, shares, tags, group invites, messages, story replies.
-
Categorized view and “mark all as read.”
Search & discovery
-
Global search for people, pages, groups, and posts.
-
Filters and sorting.
-
Trending/recommended groups and pages module.
Media handling
-
Upload pipeline for images/video with previews, progress, and failure states.
-
Automatic thumbnailing and responsive media display.
-
Basic content limits (max size/duration) with clear error messages.
Privacy & safety
-
Per-post and per-profile-field privacy.
-
Block/unblock users.
-
Report content/users/groups/pages with reason, send to moderation queue.
-
Hide/unfollow/mute content sources.
-
Basic community standards placeholder and enforcement hooks.
Admin/moderation panel (MVP)
-
Dashboard summary: users, posts, reports, growth.
-
Review reports queue: view item, take action (remove content, warn, suspend, ignore).
-
User management: search users, view profile, suspend/ban, reset flags.
-
Content takedown audit log.
Non-functional requirements
-
Responsive design, accessible UI (keyboard nav, proper contrast, ARIA).
-
Fast initial load, optimized feed rendering, lazy media loading.
-
Reliable error handling and empty states everywhere.
-
Internationalization-ready (strings separated, RTL-safe layout).
-
Secure by default: input validation, rate limiting placeholders, safe file uploads, least-privilege data access.
Key screens to implement
-
Landing + Auth (sign up/login/reset/verify)
-
Home feed
-
Create post modal/screen
-
Post detail
-
Profile (self and other)
-
Friends/requests management
-
Stories bar + viewer
-
Groups (list, create, detail)
-
Pages (create, detail)
-
Messenger (chat list, chat view)
-
Notifications
-
Search results
-
Settings (profile, privacy, security, blocked users)
-
Admin dashboard + reports queue
Data model outline (conceptual, no tech)
-
User, ProfileFieldPrivacy, Friendship, Follow
-
Post, PostMedia, Reaction, Comment, Share, Bookmark
-
Story, StoryMedia, StoryView, StoryReply
-
Group, GroupMember, GroupRole, GroupPost
-
Page, PageAdmin, PagePost, PageFollower
-
MessageThread, Message, ThreadMember, MessageReadState
-
Notification
-
Report, ModerationAction, AuditLog
Deliverables expected from the coding tool
-
Working app with the above features in MVP quality.
-
Clean, componentized UI, consistent design system, dark mode optional.
-
Clear separation of concerns and scalable structure.
-
Seed/demo data for easy testing (users, posts, groups, pages, threads).
-
Brief README describing how to run, key flows, and extension points.
Focus on correctness and completeness of user flows over edge-case perfection. Avoid naming or choosing specific technologies.
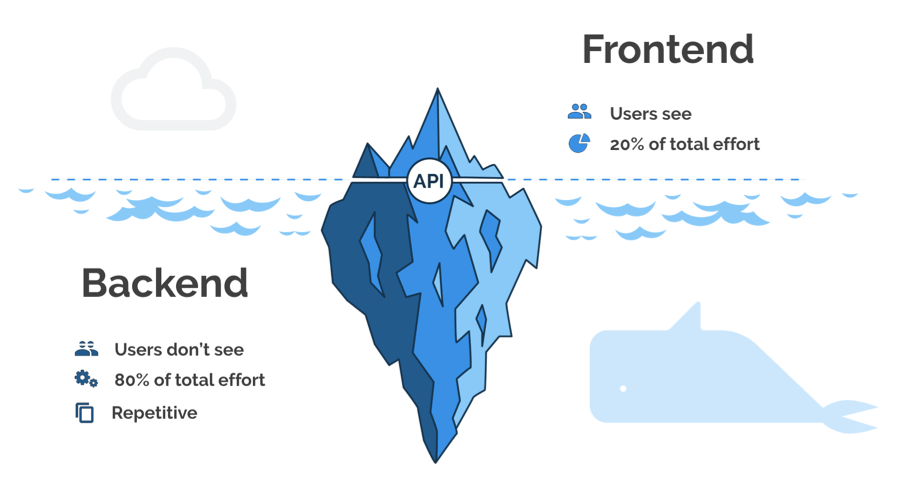
7. Create the Backend of Your App Architecture
Mobile apps are often compared to icebergs: the user only sees the visible frontend, but the backend—the submerged, massive portion—handles the vast majority of vital tasks.
The backend is responsible for generating APIs, implementing business logic, handling user authentication, and managing all data storage and retrieval.
There are two primary options for building your app’s powerful backend:
Option 1: Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Opting for a Backend as a Service (BaaS) platform is the fastest and most cost-effective way to get your app’s core server functionality operational. BaaS automates essential, time-consuming tasks like authentication, social logins, real-time data storage, and data backup.
Major Advantages of Using BaaS for an MVP:
- Back4app (A powerful, open-source-based BaaS platform ideal for scalable social app backends)
Option 2: Custom Backend
While using a Custom Backend grants you maximum flexibility and control over every line of code, it comes with significant drawbacks for an MVP:
-
Higher Cost: The cost of hiring specialized backend developers is substantially higher.
-
Longer Time-to-Market: It takes a much longer time to complete development and launch your MVP, delaying crucial market feedback.
-
Maintenance Burden: You or your team are entirely responsible for all server maintenance, scaling, security, and updates.
Conclusion: For a social media MVP, BaaS is the strategic choice to maximize speed and minimize risk.
8. Design the App’s Landing Page
The app landing page is not just a digital flyer; it’s a mission-critical component of your project’s success and your primary tool for driving user acquisition outside of the app stores. It serves as the platform for translating search interest into actual app downloads.
🎯 Key Goals of the Landing Page:
-
Display Value Proposition: Clearly and immediately showcase the core benefit your social app offers and how it solves the user’s problem (Your UVP).
-
Drive Conversion: Motivate visitors to take the single most important action: download your mobile app via the Google Play Store or Apple App Store links.
-
Establish Credibility: Increase the trust in your app and brand by providing transparency about the developers, your mission, and security/privacy policies.
Landing Page Essentials for SEO and Conversion
-
Target Keywords: Ensure the page title and headings target high-intent keywords your potential users are searching for (e.g., “new social app for creators,” “community platform for niche X”).
-
Clear Call-to-Action (CTA): Use prominent, above-the-fold CTA buttons that link directly to the app stores.
-
High-Quality Visuals: Include screenshots and short video demos that showcase the app’s clean UI/UX (from Step 2.5).
-
Social Proof: Integrate testimonials, early user reviews, or a download counter to build trust.
-
Legal Compliance: Display links to the necessary Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, which builds credibility and is required by app stores.
Treat your landing page like a crucial marketing asset; its performance directly impacts your app’s download velocity.
9. Establish an App Analytics Dashboard
our app’s analytics dashboard is the control center for your social network’s future success. It provides access to vital metrics that allow you to constantly monitor, optimize, and iterate on your live application.
By tracking user behavior, you gain insights derived directly from real-world usage. This data helps you prioritize improving existing features, adding new, relevant ones, and ruthlessly removing features that prove to be irrelevant or confusing to your users.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for a Social App
Analytics help you keep track of your goals (from Step 2.2) by providing quantitative and qualitative data. For a social network, you must focus on retention and engagement—not just downloads.
Tools and Strategy
You need to integrate an analytics SDK (Software Development Kit) from day one. Popular solutions like Google Analytics or platform-specific tools can provide this essential data.
The goal is to set up custom events that track actions unique to your platform (e.g., “shared a story,” “created a group”) so you can truly understand what drives stickiness.
10. Publish Your App to the App Stores
With your MVP fully built, tested, and validated, it’s time to publish. Before submitting, the most critical pre-publishing step is ensuring legal compliance.
Legal Pre-requisites
You must prepare and link a professional Privacy Policy and detailed Terms of Use (ToU) or Terms of Service (ToS).
Both Google and Apple require these documents, especially for apps that handle user data (like all social networks). You can purchase a reliable template, edit it for your app, or hire a legal professional.
Publishing Guidelines Comparison
The procedures differ significantly between the two major stores, primarily concerning review speed and strictness.
Crucial Update: Be aware that Google Play no longer offers instant, automatic approval. Both stores require manual review, making the pre-submission testing phase (ensuring stability and compliance) more important than ever.
Conclusion
Facebook has successfully demonstrated the massive potential of social media platforms, currently engaging over 3.07 billion active users monthly. Developing a next-generation social network is a high-risk, high-reward endeavor that demands meticulous strategic planning and precise execution.
The tasks required to create a scalable Facebook clone are undeniably complicated, placing significant demands on your time, financial resources, and technical foresight.
Remember the key takeaways from this guide:
-
Prioritize Planning: Never start coding before finalizing your high-level goals, features (MVP), and detailed prototypes.
-
Leverage Modern Tools: Utilize Backend as a Service (BaaS) like Back4app to dramatically reduce cost and time-to-market by outsourcing backend infrastructure and boilerplate coding.
-
Focus on Retention: Use the app analytics dashboard from day one to measure engagement and iterate based on real user behavior, ensuring your app stays relevant and “sticky.”
The path to creating an app like Facebook requires making strategic decisions on architecture (BaaS vs. Custom), platform (Hybrid vs. Native), and continuous optimization. By following these ten structured steps, you maximize your chance of success and build a product that can scale.
What is your opinion? Would you love to create an app like Facebook? Or do you have another app idea? Let us know in the comment section below.
If you like this article you may enjoy also the article How to make a Slack clone.
The cost for a basic social media MVP with core features (profiles, feed, messaging) generally ranges from $50,000 to $80,000, assuming you prioritize planning and use a cost-effective development strategy like Backend as a Service (BaaS) and offshore talent. A full-featured, scalable clone built custom can cost well over $500,000.
BaaS (like Back4app) is the strategic choice because it drastically reduces time-to-market and cost. It automates essential, non-differentiating features such as user authentication, data storage, real-time messaging, and server scaling, allowing your developers to focus expensive hours solely on the app’s unique frontend and features.
What are the three essential components needed before coding starts?
You must finalize three planning components before coding to save time and money: 1) A clear Unique Value Proposition (UVP) and high-level goals. 2) A definitive list of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Features. 3) Finalized Prototypes (interactive designs) that have been validated with potential users.
For the fastest and most cost-effective launch, consider the Hybrid/Cross-Platform approach, which allows you to deploy on both simultaneously. If choosing one, select Android (over 70% global share) for maximum download volume, or choose iOS (over 28% share) if your target users have higher engagement and earning potential.
What is the most important Key Performance Indicator (KPI) to track after launch?
The most important KPI for a social app is User Retention (e.g., D7/D30 Retention Rates), followed closely by Daily Active Users (DAU). While downloads matter (Acquisition), if users aren’t returning and engaging, your social network will fail to achieve the critical network effects needed for growth.