Backend as a Service (BaaS) Guide 2026: Tools, Pros, Cons & Trends
Updated: November 2025
It is the classic “Builder’s Dilemma”: You have a brilliant idea for an application that solves a real user problem. You have the user interface sketched out and the frontend framework selected. But then, reality hits.
Before you can ship a single feature, you have to spend weeks—sometimes months—configuring servers, setting up database clusters, writing boilerplate authentication code, and worrying about infrastructure security.
For many developers and founders, this backend friction is where great ideas go to die.
Enter Backend as a Service (BaaS). In 2026, BaaS has evolved from a simple prototyping tool into a robust cloud model that automates the heavy lifting of backend infrastructure.
By outsourcing responsibilities like database management, user authentication, and push notifications, developers can focus entirely on the frontend and user experience.
The core value proposition is simple: Velocity. BaaS reduces engineering overhead and significantly accelerates time-to-market, allowing startups to launch MVPs in days rather than months.
Contents
- 1 What is Backend as a Service (BaaS)?
- 2 BaaS vs. The World (Comparison Section)
- 3 Top Backend as a Service Providers (2026 Comparison)
- 4 The Pros and Cons of a Backend as a Service (Honest Review)
- 5 Decision Matrix: When should you use BaaS?
- 6 Market Size & Trends in BaaS
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 FAQ
- 9 What is Backend as a Service (BaaS) and why use it?
- 10 What is the difference between BaaS and Serverless (FaaS)?
- 11 Which are the top Backend as a Service providers in 2026?
- 12 When should a startup use BaaS instead of a custom backend?
- 13 How does AI integration impact Backend as a Service?
What is Backend as a Service (BaaS)?
Backend as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides developers with a ready-made, scalable backend infrastructure.
Instead of provisioning servers and writing server-side boilerplate code from scratch, developers use APIs and SDKs to instantly integrate core functionalities—such as databases, authentication, file storage, and serverless functions—directly into their frontend applications.
This allows teams to focus entirely on the user interface and client-side logic.
The “Restaurant” Analogy
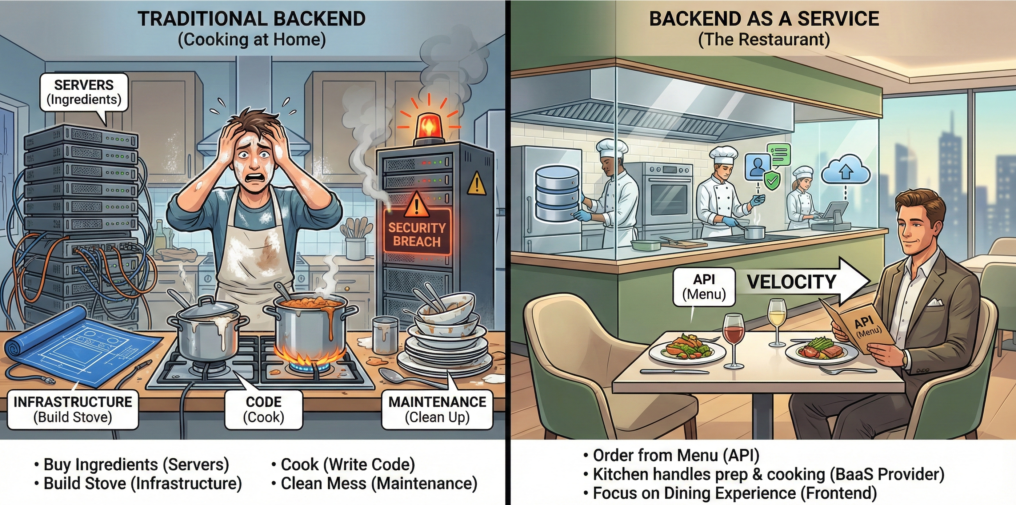
To understand BaaS, think of the difference between cooking a meal at home versus ordering at a restaurant .
- Traditional Backend Development (Cooking at Home): You have to buy the ingredients (servers), build the stove (infrastructure), cook the food (write the code), and clean up the mess (maintenance/security).
- Backend as a Service (The Restaurant): You simply order from the menu (API). The kitchen (BaaS provider) handles the prep, cooking, scaling, and cleaning. You just focus on the presentation and the dining experience (the Frontend).
Core Components
BaaS providers offer a suite of pre-built, cloud-based features accessed via APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and SDKs (Software Development Kits). A standard BaaS platform in 2026 includes:
- Databases: Scalable NoSQL or SQL (Relational) databases that offer real-time data synchronization across clients.
- Serverless Functions: The ability to execute custom business logic (Cloud Code) in the cloud without provisioning servers.
- APIs (GraphQL & REST): Instead of manually coding endpoints, platforms like Back4App automatically generate production-ready REST and GraphQL APIs based on your database schema, allowing for immediate data access and manipulation.
- Authentication: Ready-made systems for user registration, login (email/password), social logins (Google, Apple, GitHub), and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- Cloud Storage: Secure hosting for user-generated content like images, videos, and documents, often paired with a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- Notifications: Infrastructure to send push notifications, emails, and SMS to engage users.
- AI Features (Agents & MCP): Modern BaaS platforms now integrate AI Agents that act as “Co-DevOps” assistants to provision infrastructure via natural language prompts. New standards like the Model Context Protocol (MCP) allow these agents to connect directly to IDEs (like Cursor or VS Code) to build and manage your backend context-aware.
BaaS vs. The World (Comparison Section)
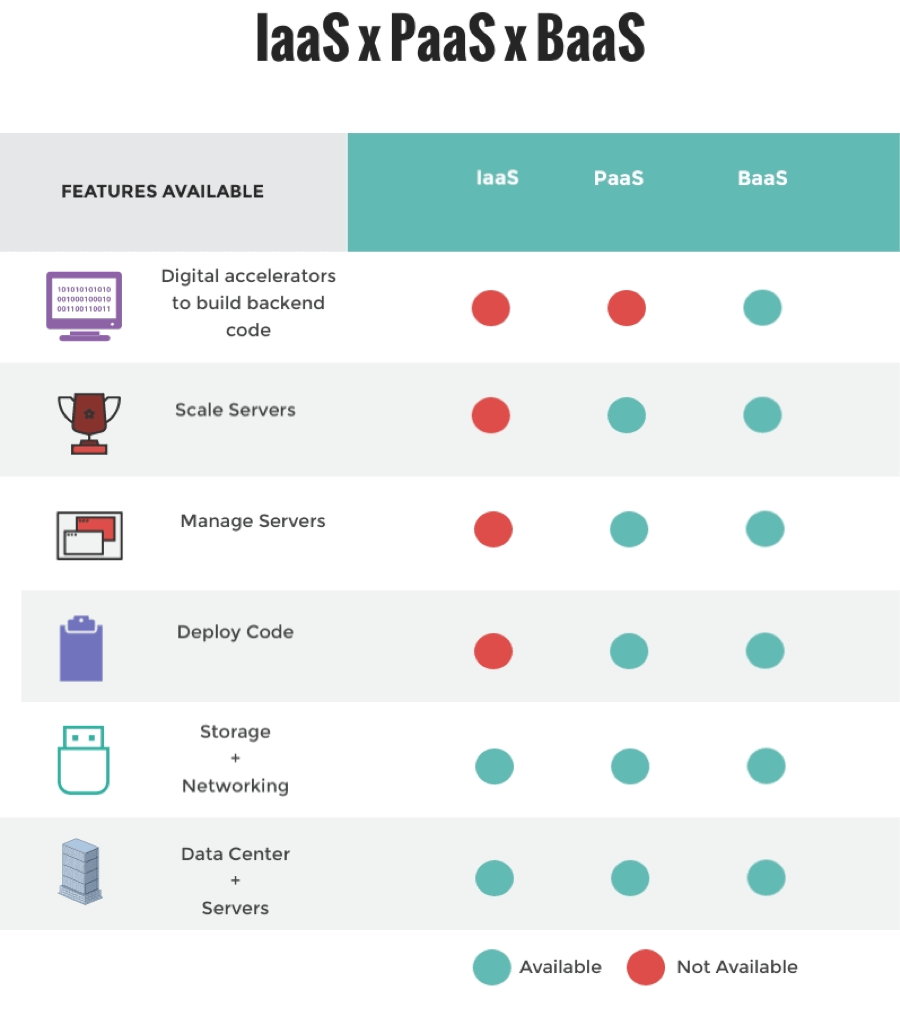
To establish the right tech stack, it is crucial to differentiate BaaS from other cloud models.
BaaS vs. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
While BaaS is built on top of cloud infrastructure, it abstracts it away completely.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): You rent the raw “building blocks” like virtual machines, storage, and networks. You are responsible for installing the operating system, configuring the database, and managing security patches.
- BaaS: The provider manages the entire server layer for you. You don’t configure the OS or install software; you just connect your frontend to ready-to-use cloud services.
BaaS vs. Serverless (FaaS)
While BaaS uses serverless technology, they are not the same.
- Serverless (Function as a Service): You write the discrete functions (logic) that run in response to events. You are responsible for the code, but not the server.
- BaaS: The provider gives you pre-written logic and services. You don’t write the code for “Login” or “Save to Database”; you just call the API that already exists.
BaaS vs. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- PaaS (e.g., Heroku, Render): Provides a platform to deploy your custom code. It manages the runtime and deployment, but you must still write the backend application logic.
- BaaS (e.g., Back4app, Firebase): Abstracts away the runtime entirely. It provides the data and logic layers directly, often eliminating the need for a “backend application” in the traditional sense.
BaaS vs. Custom Backend
The trade-off here is Control vs. Speed. A custom backend (coding everything from scratch on AWS/Azure) offers infinite flexibility but requires a dedicated team to manage uptime, security patches, and scaling. BaaS sacrifices some granular control for massive gains in development speed and reduced costs.
Top Backend as a Service Providers (2026 Comparison)
While the market is flooded with tools, five platforms dominate the conversation in 2026. Here is how they stack up, based on architecture, data flexibility, and developer experience.
1. Back4App (The AI-Native Powerhouse)
Best For: Developers who want the speed of NoSQL with the power of SQL relationships, and those looking to leverage AI for backend generation.
Built on top of open-source technologies, Back4App eliminates the trade-off between “easy” and “powerful.”
It creates a “Low-Code/No-Code” bridge where you can manage complex data relationships (like joins and aggregates) as easily as a spreadsheet—something traditional NoSQL stores struggle with.
In 2026, it stands apart with its AI Agent, which allows you to generate schemas, code, and app logic via natural language prompts.
- Key Features: AI-powered backend generation, Real-time Database (Live Queries), Auto-generated GraphQL & REST APIs, Docker container support.
- Pros: Open-source foundation (No vendor lock-in), relational data queries, predictable pricing, and seamless scalability.
- Pricing: Generous Free Tier; scalable Pay-as-you-go, Dedicated plans. MVP plan starts at $25/month.
2. Firebase (The Google Standard)
Best For: Mobile-first MVPs and teams deeply integrated into the Google Cloud ecosystem.
Firebase is the giant of the industry. Acquired by Google in 2014, it offers a mature, polished suite of tools that cover the entire app lifecycle, from authentication to analytics. Its JSON-based NoSQL database (Firestore) is incredibly fast for simple data structures.
- Key Features: Cloud Firestore, Google Analytics, Crashlytics, Remote Config.
- Pros: Massive community support, high-quality documentation, and seamless integration with other Google services.
- Pricing: Spark Plan (Generous Free Tier with limits); Blaze Plan (Pay-as-you-go based on usage, required for Cloud Functions).
3. Supabase (The Postgres Option)
Best For: Postgres purists and developers who want an open-source alternative to Firebase.
Supabase is an open-source backend suite designed to unlock the full potential of PostgreSQL. By constructing its architecture directly on top of this robust relational database, it provides developers with familiar SQL tooling alongside modern necessities like instant REST and GraphQL APIs, real-time data subscriptions, and secure authentication.
- Key Features: Full Postgres Database, Row Level Security (RLS), Vector embeddings for AI, Real-time subscriptions.
- Pros: No vendor lock-in (self-hostable), industry-standard SQL allows for complex queries and data integrity.
- Pricing: Free Tier (Available for limited projects); Pro Plan starts at $25/month per project.
4. Appwrite (The Developers’ Cloud)
Best For: Developers who prioritize privacy, control, and a clean Developer Experience (DX).
Appwrite focuses on being easy to use and move around. It is packaged so that you can run it yourself on almost any machine, from a small hobby computer to a large enterprise server.
It hides the complex machinery of the backend, giving developers simple commands to build their apps quickly
- Key Features: Docker-based architecture, Auth, Database, Storage, and Functions in one binary.
- Pros: Complete data ownership (privacy-focused), runs anywhere Docker runs, very intuitive API design.
- Pricing: Free Tier (Available for limited projects); Pro Plan starts at $25/month per project.
5. Backendless (The Visual Low-Code Option)
Best For: Developers and teams who prefer visual builders over writing code.
Backendless bridges the gap between a BaaS and a No-Code platform. It offers a “Codeless” logic builder that lets you design APIs and business logic visually.
It is a strong choice for teams that may not have deep backend engineering resources but need complex functionality.
- Key Features: Visual UI Builder, Codeless Logic (visual programming), Database, Real-time.
- Pros: Extremely fast for non-coders to build complex logic; includes a frontend UI builder.
- Pricing: Free Tier (Unlimited API calls/month but capped at 50/minute); Scale Plan starts at $15/month.
The Pros and Cons of a Backend as a Service (Honest Review)
The Good (Pros)
- Speed: “Time to Market” is the #1 driver. You can skip months of boilerplate coding.
- Cost: For startups and low-traffic apps, BaaS is often cheaper than hiring a backend engineer. Most providers offer generous free tiers.
- Maintenance: You don’t need to worry about server patching, uptime, or infrastructure security updates—the provider handles it all.
The Bad (Cons)
- Vendor Lock-in: This is the most critical risk. Proprietary platforms use specific data structures (like Firebase’s specific NoSQL format) that make exporting your data and logic to another platform difficult.
- Scaling Costs: Pricing is typically usage-based (paying for API calls, storage, and data transfer). While this model offers great flexibility for early-stage apps, it means that as your user base grows, your infrastructure costs will naturally scale alongside your success, requiring you to monitor usage more closely than with a fixed-cost server.
- Flexibility: You are limited to the features the provider offers. If you need a highly specialized feature (e.g., complex video encoding pipelines) that the BaaS doesn’t support, you may hit a wall
Decision Matrix: When should you use BaaS?
✅ Green Light (Use BaaS):
- MVPs and Prototypes: When validating an idea is more important than architectural purity.
- Mobile & Web Apps: Ideal for Flutter/React Native mobile apps requiring offline sync, as well as modern Web Apps (React, Vue, Next.js) that need instant backend connectivity without server bloat.
- Standard CRUD Apps: Applications that primarily create, read, update, and delete data (e.g., social networks, to-do lists, e-commerce).
- AI & “Vibe Coding” Projects: If you are using AI coding assistants (like Cursor or VS Code) and want to generate your backend schema and logic via prompts rather than writing manual boilerplate.
❌ Red Light (Build Custom):
- Heavy Compute Apps: Apps requiring intensive processing like AI model training or video rendering.
- Complex Legacy Integrations: If you need to connect to a 20-year-old on-premise mainframe, a cloud BaaS might struggle.
- Strict Regulatory Requirements: Enterprise apps requiring 100% on-premise control where data cannot leave a specific physical location (unless using a self-hosted BaaS).
Market Size & Trends in BaaS
The global Backend as a Service (BaaS) market is experiencing explosive growth, driven by the increasing demand for rapid mobile and web application development.
The market was valued at approximately $8.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $31.1 billion by 2030, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 24.3%.
Other estimates specifically focusing on the Mobile Backend as a Service (MBaaS) segment project an even steeper trajectory, anticipating a rise from $37.08 billion in 2025 to over $105 billion by 2032, fueled by the proliferation of 5G, IoT devices, and the need for cost-efficient, scalable cloud infrastructure.
This surge underscores a fundamental shift in the industry: enterprises and startups alike are moving away from building custom backend infrastructure in favor of managed, scalable solutions that reduce time-to-market.
- AI Integration: The biggest trend in 2026 is the “AI-native” backend. Providers are integrating Vector Databases and Large Language Model (LLM) hooks directly into the BaaS, allowing developers to build AI features like semantic search and chatbots without managing a separate vector store.
- Rise of Edge Computing: To reduce latency, BaaS providers are moving logic closer to the user. Integration with edge networks allows backend logic to execute in milliseconds, regardless of where the user is located.
- The Open Source Shift: As developers become wary of price hikes and lock-in, the market is shifting toward open-source options. This “Buy or Build” hybrid model offers the best of both worlds.
Conclusion
Backend as a Service is no longer just a tool for hackathons and prototypes; it is a mature architectural choice for scaling businesses. It essentially commoditizes the backend, treating it as a utility rather than a differentiator.
In 2026, the question for most new projects shouldn’t be “How do I build a backend?” but “Which BaaS provider lets me move the fastest?” Don’t reinvent the wheel.
Pick a provider, avoid the lock-in traps by choosing flexible data structures, and ship your app today.
FAQ
What is Backend as a Service (BaaS) and why use it?
Backend as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud model that automates backend infrastructure, providing pre-built features like databases, authentication, and file storage via APIs. It allows developers to focus entirely on frontend user experience, significantly increasing development velocity and reducing time-to-market for MVPs.
What is the difference between BaaS and Serverless (FaaS)?
While BaaS uses serverless technology, they are distinct. Serverless (Function as a Service) requires developers to write their own backend logic functions. In contrast, BaaS provides pre-written logic and services (like “Login” or “Save Data”) that are instantly accessible via APIs, abstracting away the coding of standard backend features.
Which are the top Backend as a Service providers in 2026?
The top BaaS providers in 2026 include Back4App (known for AI-native backend generation), Firebase (best for Google ecosystem integration), Supabase (the top SQL/Postgres alternative), Appwrite (best for self-hosting and privacy), and Backendless (ideal for visual low-code development).
When should a startup use BaaS instead of a custom backend?
Startups should use BaaS for MVPs, prototypes, and standard CRUD applications where speed is the priority. It is ideal for mobile apps requiring out-of-the-box offline sync and push notifications. However, heavy compute apps or those requiring strict legacy integrations are better suited for custom backends.
How does AI integration impact Backend as a Service?
In 2026, AI-native BaaS platforms integrate AI Agents and the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This allows developers to provision infrastructure, generate database schemas, and manage context-aware backend logic using natural language prompts directly within their IDEs.



